Description:
Given a singly linked list, you are supposed to rearrange its elements so that all the negative values appear before all of the non-negatives, and all the values in [0, K] appear before all those greater than K. The order of the elements inside each class must not be changed.
For example, given the list being 18→7→-4→0→5→-6→10→11→-2 and K being 10, you must output -4→-6→-2→7→0→5→10→18→11.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains the address of the first node, a positive N (≤ 105) which is the total number of nodes, and a positive K (≤ 103). The address of a node is a 5-digit nonnegative integer, and NULL is represented by −1.
Then N lines follow, each describes a node in the format:
Address Data Next
where Address is the position of the node, Data is an integer in [−105 ,105 ], and Next is the position of the next node. It is guaranteed that the list is not empty.
Output Specification:
For each case, output in order (from beginning to the end of the list) the resulting linked list. Each node occupies a line, and is printed in the same format as in the input.
Sample Input:
00100 9 10
23333 10 27777
00000 0 99999
00100 18 12309
68237 -6 23333
33218 -4 00000
48652 -2 -1
99999 5 68237
27777 11 48652
12309 7 33218
Sample Output:
33218 -4 68237
68237 -6 48652
48652 -2 12309
12309 7 00000
00000 0 99999
99999 5 23333
23333 10 00100
00100 18 27777
27777 11 -1
思路:
思路很简单,遍历比较与K和0的关系即可。一开始用vector存储的是node,这样作insert操作消耗时间很大,优化为存储地址值(下标)。
坑点:
但是被PTA的编译器坑了,这题花了很多时间找bug
一开始for循环写的是
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
int add;
cin >> add >> list[add].data >> list[add].next;
}
在自己的ide运行没毛病,换到pat的编译器(g++6.5.0)就。。。
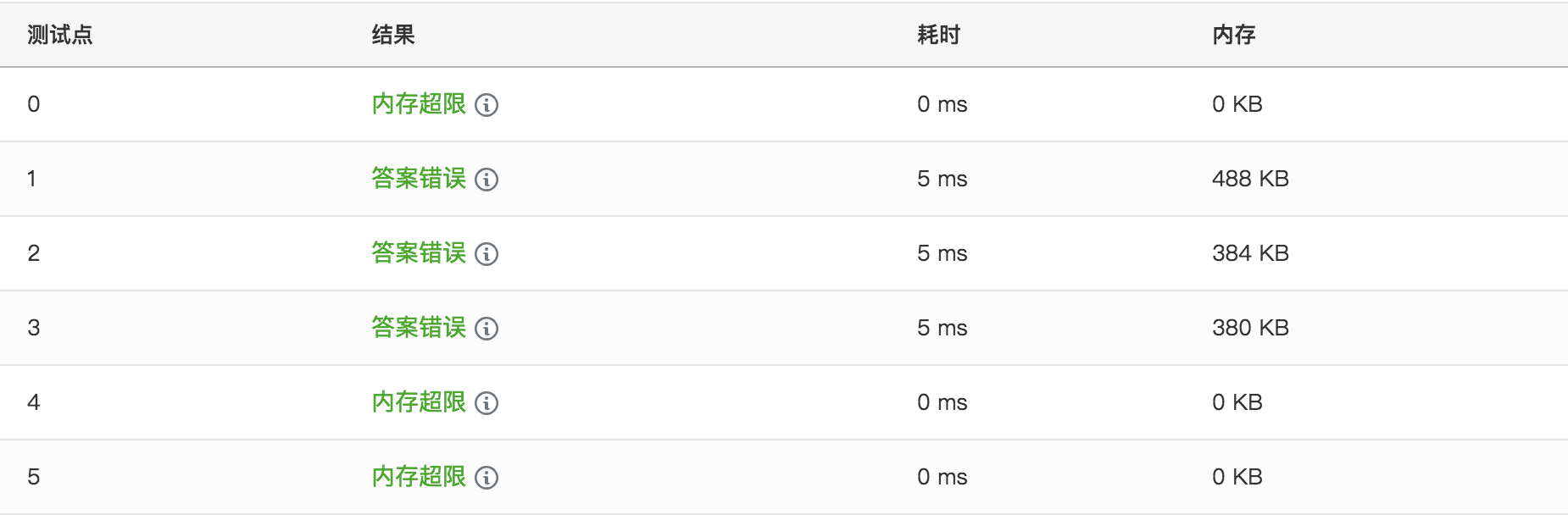
想了很久,把for循环改了就Accepted了
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
int add;
cin >> add;
cin >> list[add].data >> list[add].next;
}
个人理解是pat的编译器对一个输入流一次性读入数据并赋值,这样add的值读入之后并不是list[add]中的add。
查了一下我使用的xcode的c编译器是使用的clang,把PTA的编译器换成clang++6.0.1
也可以了。。-_-||
code:
#include<iostream>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 100010;
struct node{
int data;
int next;
}list[maxn];
int main(){
int head, N, K;
cin >> head >> N >> K;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
int add;
cin >> add >> list[add].data >> list[add].next;
}
//从头结点开始 分别记录 小于0的部分 [0,K]的部分 大于K的部分 的地址(比记录node消耗空间和时间都少)
vector<int> negativePart;
vector<int> smallPart;
vector<int> bigPart;
while (head != -1) {
if (list[head].data < 0)
negativePart.push_back(head);
else if(list[head].data <= K)
smallPart.push_back(head);
else
bigPart.push_back(head);
head = list[head].next;
}
//把后两个部分的地址都插入第一个部分后面
negativePart.insert(negativePart.end(), smallPart.begin(), smallPart.end());
negativePart.insert(negativePart.end(), bigPart.begin(), bigPart.end());
for (int i = 0; i < negativePart.size(); ++i) {
if (i != negativePart.size() - 1) {
printf("%05d %d %05d\n", negativePart[i], list[negativePart[i]].data, negativePart[i+1]);
}else printf("%05d %d -1\n", negativePart[i], list[negativePart[i]].data);
}
return 0;
}